Polycystic Ovary Syndrome or PCOS affects millions of women worldwide, with symptoms that include difficulties with fertility and getting pregnant. For any woman who wants to start a family, switching medication and taking care of yourself while pregnant might sound hard.
But as long as patients are informed and take proactive steps, many women with PCOS can successfully conceive and build their families. Klinik Casabrina can help you start your journey by answering your questions and supporting you through your pregnancy.
What is PCOS?
PCOS is a hormonal disorder characterized by irregular periods, excess androgen levels, and the presence of ovarian cysts. These hormonal imbalances can disrupt ovulation, making it challenging for women with PCOS to conceive naturally.
Understanding the possible complications before you get pregnant can help prepare you to make the right decisions and take care of your health throughout your pregnancy. With the right diet and lifestyle choices, you’ll be able to give birth to a healthy future baby.
Impact of PCOS on Pregnancy
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) can have various impacts on pregnancy, affecting both the mother and the developing baby. Expectant mothers should be informed by their doctors to ensure proper monitoring and management throughout pregnancy.
Increased Risk of Gestational Diabetes (GDM)
- Women with PCOS have a higher likelihood of developing gestational diabetes during pregnancy compared to women without PCOS.
- Insulin resistance, a common feature of PCOS, contributes to glucose intolerance, which can lead to gestational diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes increases the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby, including macrosomia (large birth weight), birth injuries, and the need for cesarean delivery.
Increased Chance of Preterm Birth
- Women with PCOS have a slightly higher risk of delivering prematurely (before 37 weeks of gestation) compared to women without PCOS.
- Preterm birth increases the risk of health problems for the baby, including respiratory distress syndrome, developmental delays, and long-term health issues.
- The exact mechanism underlying the association between PCOS and preterm birth is not fully understood but may involve factors such as hormonal imbalances and inflammation.
Higher Likelihood of Cesarean Section (C-section):
- Due to various factors such as gestational diabetes, hypertension, and fetal distress, women with PCOS may have an increased likelihood of requiring a cesarean section delivery.
- C-sections may be performed for medical reasons to ensure the safety of the mother and the baby when vaginal delivery is not feasible or safe.
- It’s essential for women with PCOS to discuss birthing options with their healthcare providers and be prepared for the possibility of a C-section if deemed necessary.
Higher Risk of Hypertension and Preeclampsia:
- Pregnant women with PCOS are at an increased risk of developing hypertension (high blood pressure) and preeclampsia, a serious pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and organ damage.
- Preeclampsia can lead to complications such as eclampsia (seizures), stroke, and organ failure if left untreated.
Close monitoring during pregnancy, including regular prenatal check-ups, ultrasounds, and fetal monitoring, can help detect and address any potential complications early on.
Tips for Conceiving with PCOS
Ovulation Tracking: Monitoring your menstrual cycle is crucial for women with PCOS trying to conceive. While irregular periods can make predicting ovulation challenging, using tools such as ovulation predictor kits, tracking basal body temperature, and monitoring cervical mucus consistency can help identify fertile windows.
Medical Intervention: Seeking assistance from a fertility specialist can also help. Fertility treatments such as ovulation induction with medications like Clomid or Letrozole, intrauterine insemination (IUI), and in vitro fertilization (IVF) can help overcome ovulatory issues associated with PCOS.
Weight Management: Obesity and PCOS often coexist and make fertility issues worse. Losing even a modest amount of weight can improve ovulation and increase the chances of conception in overweight or obese women with PCOS. A personalized weight management plan developed with the guidance of a healthcare professional can be beneficial.
Supplements: Some women with PCOS may benefit from certain supplements known to support fertility, such as inositol, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids. Consult with our doctors before starting any supplements to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Managing PCOS during Pregnancy

Regular Prenatal Care: Women with PCOS should receive comprehensive prenatal care. This includes regular prenatal check-ups, screenings for gestational diabetes and other complications, and monitoring fetal growth and well-being.
Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial for managing PCOS during pregnancy. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, staying physically active (with guidance from healthcare providers), managing stress levels, and getting adequate rest.
Medication Management: Some women with PCOS may continue taking certain medications during pregnancy, while others may need adjustments or discontinuation of certain medications.
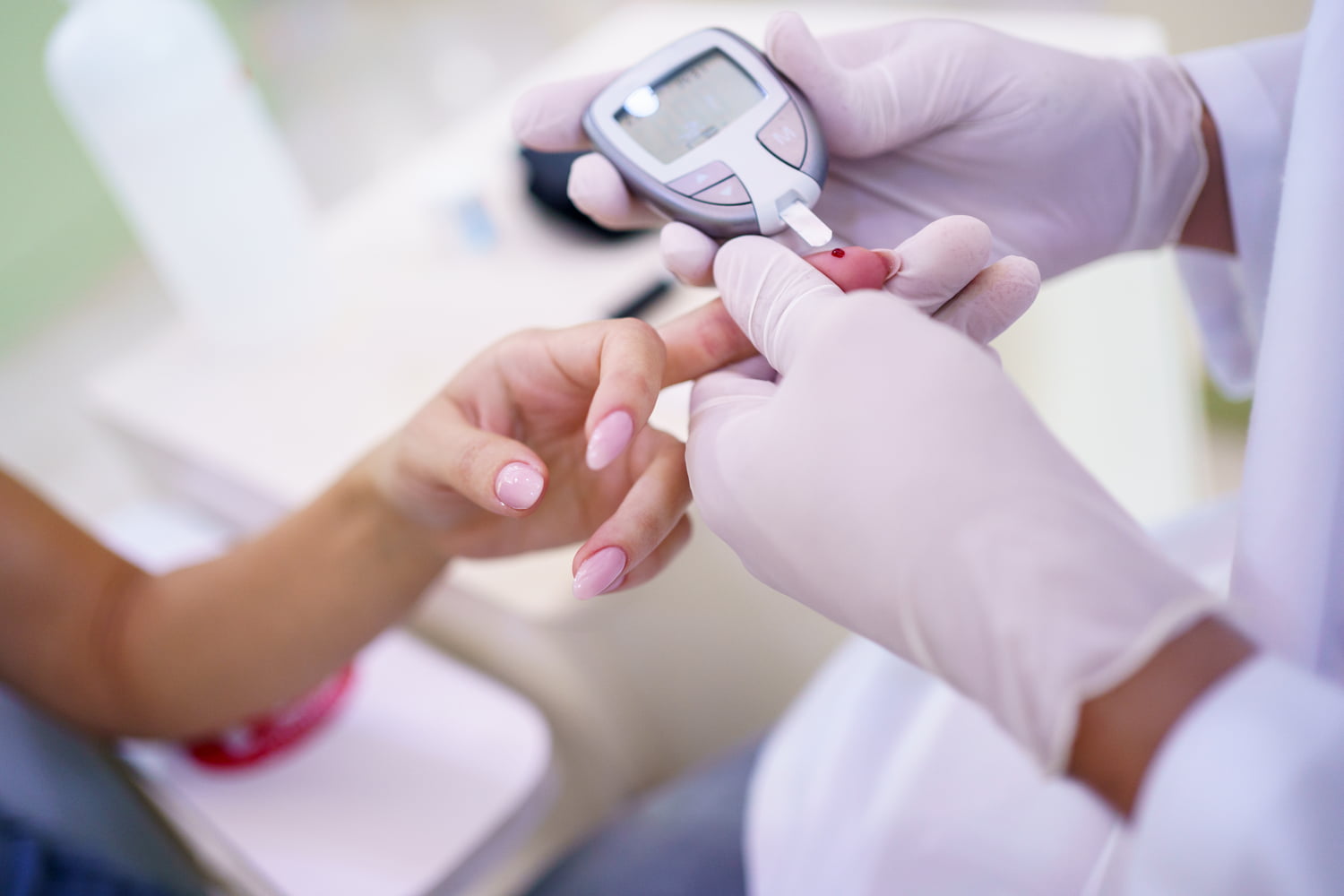
Blood Sugar Monitoring: Women with PCOS and gestational diabetes should monitor their blood sugar levels regularly and follow any recommended dietary and lifestyle modifications to keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
Support for PCOS at Klinik Casabrina
Navigating PCOS and pregnancy can be complex, but it’s essential to approach it with patience. Every woman’s journey is unique, and what works for one may not work for another. By staying informed, seeking support, and exploring available options, many women with PCOS can fulfill their dreams of becoming mothers.
Klinik Casabrina strives to help you with open communication, adherence to prenatal care guidelines, and a commitment for your healthy lifestyle. Visit our clinic near Senawang today for a pregnancy consultation!